Last updated: 30-01-2024
Using Botox to treat migraines
Botox is normally known as a way to treat wrinkles. However, it can also help to manage migraines.
Botox works by blocking signals in the brain that send messages between nerve cells. Doing so stops muscles from contracting. This helps to lessen the pain signals that are a part of migraines.
Botox is very good at reducing the amount of times migraines occur. It also makes them less severe when they do happen.
How did people find out about this?
Botox was originally a well-known way to treat wrinkles. The fact it could be used to treat migraines was discovered by accident.
Botox patients said they had fewer headaches after having Botox treatments. This led to Botox being researched as a treatment for migraine headaches. The FDA approved Botox as a treatment for long-term (chronic) migraines in 2010.
Botox shortens the length of a migraine. It has few side effects and is very safe. It has worked well where other treatments have failed.
Who can be treated with Botox for migraines?
Botox can be used to treat chronic migraine sufferers. A chronic migraine is a headache for 15 or more days a month, with typical migraine symptoms on at least eight of those days.
People who take Botox for migraines have usually tried other treatments that have not worked.
Can you have Botox therapy for your migraine?
You may or may not be suitable for Botox treatment for your migraine. Your doctor will need to check your history. They will look at how often you get migraines and how severe they are. They will also look at any other treatments you have had for your migraines.
Your doctor will also consider other issues. These include whether your headaches are caused by taking too much medication or because you suffer from other conditions.
Can you get Botox on the NHS?
In the UK, you can get Botox on the NHS. However, you have to meet certain conditions.
To receive Botox on the NHS, you must have chronic migraines that could not be prevented by other medicines. You must have tried at least three other medicines to prevent your migraines.
You will normally need to be referred by your GP to a specialist doctor.
The Botox treatment process
Preparing for your Botox injections
You will need to tell your doctor all your medical history. This includes any allergies or muscle and nerve conditions. You also need to tell your doctor about any medicines you are taking.
You should also be realistic about how much the treatment will help. While it is very good at treating migraines, Botox is not a miracle cure.
What to expect when getting Botox
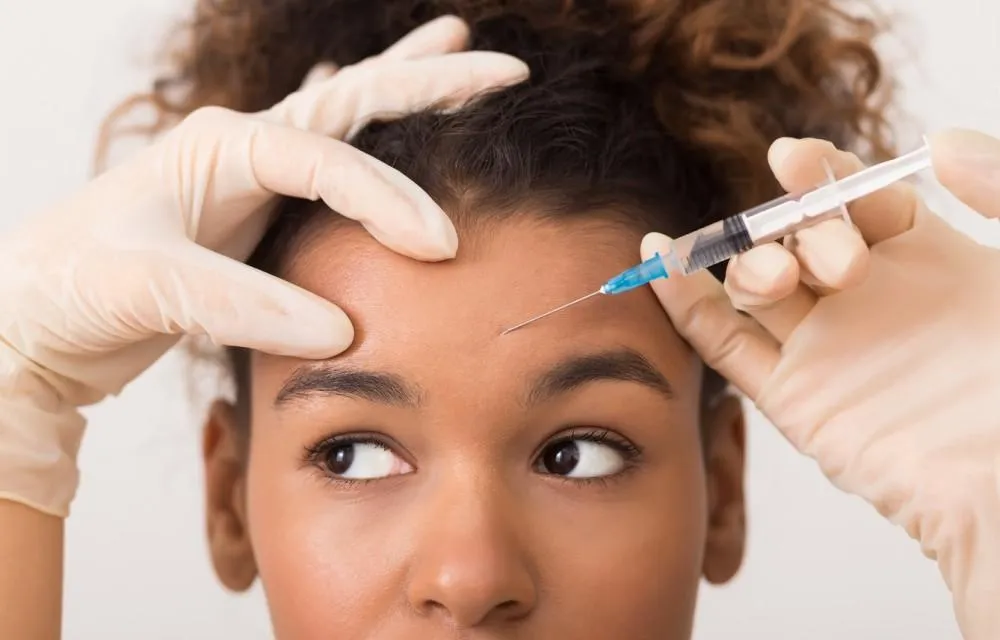
You will have thirty to forty injections in your head and neck every 12 weeks.
The process is very quick. You do not need to be numbed up, and you can do all your normal activities straight away.
After your Botox treatment
After your treatment, avoid rubbing the injected area for 24 hours. Botox usually has only minor side effects, and they don’t last long.
Follow up with your doctor to make sure the treatment has worked well. Your doctor may make changes to your treatment plan if needed.
Success stories: real-life patients
Several studies have shown how good Botox is at treating migraines.
A 2021 study of patients talked about people who had received Botox for migraines. The migraine sufferers said that Botox had an impact on their lives.
In 2019, the REPOSE study looked at using Botox to treat chronic migraines. The study found that Botox reduced the number of days the headaches lasted. It also showed that Botox treatments improved the migraine sufferers’ daily lives.
A 2008 study looked at using Botox to treat cervical dystonia. This is a condition where the muscles in your neck contract uncontrollably. After the Botox treatment, the patients said they had less pain, fewer headaches and a better quality of life. They also needed to take less medication and could manage their emotions better.
In 2016, a study looked at the use of Botox to treat chronic migraines. Again, the study showed that the patients had fewer migraine days per month. They also needed to take less medication to treat their symptoms. In this study, the Botox was taken over a long period. This proves that it is a good way to treat chronic migraines.
What if Botox doesn't work?
Sometimes, Botox doesn’t work. There are other treatments, such as medicines to prevent migraines. Patients can also try making lifestyle changes or having treatments like massage or biofeedback.
Risks of Botox treatments
Common side effects
The most common side effects are neck pain, headache or temporary muscle weakness where you have been injected. These are usually mild and get better on their own.
Rare but serious side effects
Serious side effects of Botox are rare. They happen when the effects of the toxin spread. The symptoms of this are muscle weakness, problems with your eyesight, or difficulty breathing.
If you have any of these symptoms after having Botox treatment, seek medical help straight away.
FAQs: Botox for migraines
How much does Botox for migraines cost in the UK?
The cost of Botox for migraines in the UK varies. The cost of private treatment depends on the number of injections needed and the healthcare provider's fees.
On average, private treatment costs range from £150 to £350 per session. However, the NHS often covers Botox treatment for chronic migraines. For the NHS to cover treatment, the migraines and the patient have to meet certain criteria.
Does Botox help with migraines?
Yes, several studies have shown that Botox helps with migraines. The FDA has approved its use to prevent chronic migraines. Chronic migraines are headaches that occur 15 or more days a month.
Botox works by blocking the pain signals from your brain. This reduces the frequency and severity of migraine attacks.
What happens during Botox treatment for migraines?
You will have thirty to forty injections in the head and neck area. These are given by a doctor or other healthcare professional.
Each treatment usually takes about 15–20 minutes. Patients usually have Botox injections every 12 weeks. However, this can vary based on how they respond to the treatment.
Who can have Botox treatment for migraines?
Botox is recommended for adults who have chronic migraines. A chronic migraine is a headache for 15 or more days a month, with typical migraine symptoms on at least eight of those days.
Talk to your GP to find out if Botox treatment might work for your migraines.
What are the common side effects?
The common side effects of Botox are neck pain, headache, tiredness. Patients can sometimes get eye problems such as drooping eyelids or double vision.
Most side effects are mild and only last for a short while. Talk to your GP if you have any unusual symptoms after Botox treatment.
Conclusion
Botox is a very good treatment for migraines. It helps to improve sufferers’ quality of life. As more research is done, it is likely that we will find more ways to use Botox to treat headaches and other conditions.